Study of two corks species as natural biosorbents for five selected pesticides in water.
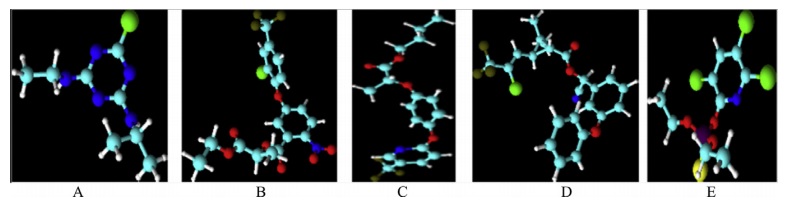
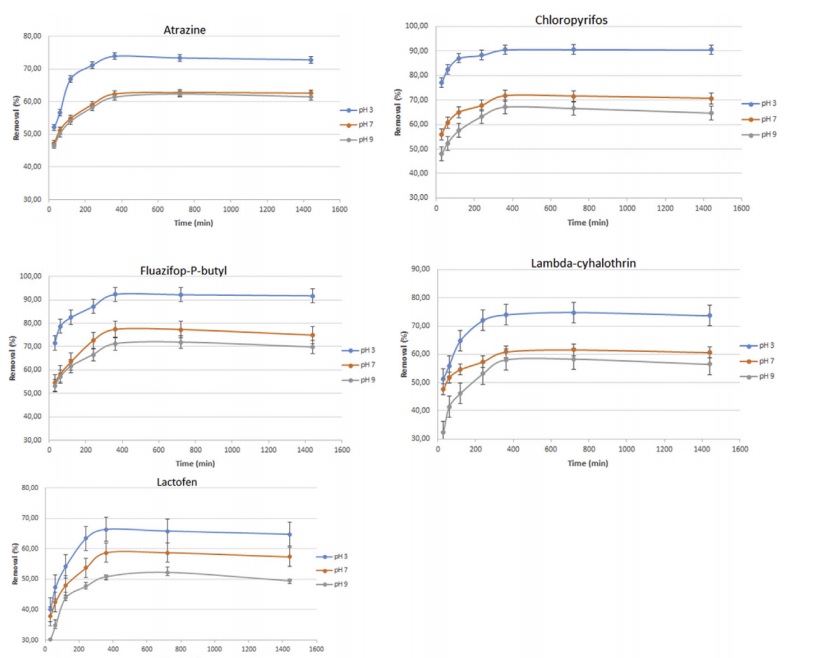
The present study evaluates biosorption efficiencies of pesticides atrazine, fluazifop-P-butyl, lactofen, lambda-cyhalothrin and chloropyrifos on corks of Quercus cerris and Quercus suber trees. The studies were carried out in batch and effects of pH (3, 7 and 9), temperature (10, 20, 30 and 40 °C), and time (0, 200, 400, 600, 800, 100, 1200, and 1400 minutes) on adsorption were measured. Pesticide analyzes were performed with an Ion-trap Mass Spectrometer following the SANCO/10232/2006 EU extraction protocol for pesticides. The results show that the highest adsorption efficiency (80% and 70%) of the pesticides was found at pH 3, 30 °C and 360 minutes. The adsorption kinetics of pesticides followed pseudo-second order and pseudo-first order kinetics. The results obtained in this study show that Q. cerris and Q. suber corks can be used to develop efficient and economical cork-based alternatives for the treatment of environments contaminated with pesticides
Link to the article: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2019.e01189